How Often Do Commercial Properties Need PAT Testing? (UK Law Explained)
Electrical safety is crucial for any property, particularly commercial properties where the equipment used on a day-to-day basis is often essential for business operations. To ensure that the electrical appliances and systems in a commercial property are safe to use, it’s necessary to carry out regular checks, one of the most important being Portable Appliance Testing (PAT Testing).
In this comprehensive guide, we will explain what PAT testing is, why it’s essential for commercial properties, and most importantly, how often commercial properties in the UK need to conduct PAT testing. Additionally, we will explore the legal requirements surrounding PAT testing, helping you stay compliant and avoid costly penalties.
Table of Contents:
What is PAT Testing?
Why is PAT Testing Important for Commercial Properties?
Legal Requirements for PAT Testing in the UK
How Often Should Commercial Properties Have PAT Testing?
Factors Affecting the Frequency of PAT Testing
What Does a PAT Test Involve?
The Consequences of Failing to Carry Out PAT Testing
Choosing a Qualified PAT Testing Service
Costs Associated with PAT Testing
Best Practices for Maintaining Electrical Safety Between PAT Tests
Conclusion
1. What is PAT Testing?
Portable Appliance Testing (PAT Testing) is the process of inspecting and testing electrical appliances and equipment to ensure they are safe to use. The primary goal is to reduce the risk of electrical hazards, including shocks, fires, and other electrical accidents, by ensuring that appliances are in good working order.
PAT testing usually involves:
Visual Inspections: A qualified electrician or technician will check for visible signs of damage, wear, or defects, such as frayed wires, scorch marks, or exposed conductors.
Electrical Testing: Appliances are subjected to tests like earth continuity testing, insulation resistance testing, and functional checks to ensure the appliance is safe to use.
Commercial properties use a variety of electrical appliances—ranging from computers and vending machines to power tools and kitchen equipment—that need to be checked regularly for safety.
2. Why is PAT Testing Important for Commercial Properties?
For commercial properties, electrical safety is paramount. Not only does it protect employees and customers from potential harm, but it also safeguards the property itself from fire risks and electrical accidents. Below are some key reasons why PAT testing is important:
Health and Safety Compliance
Employers have a legal responsibility to ensure the health and safety of their employees and anyone who enters their property. This includes ensuring that all electrical equipment is safe to use. By performing regular PAT testing, businesses can demonstrate compliance with Health and Safety at Work Act 1974, which requires employers to take steps to prevent electrical accidents.
Minimizing the Risk of Electrical Fires
Electrical fires are a serious risk in commercial properties, especially those that use heavy-duty equipment or have a large number of electrical appliances. Faulty appliances are one of the leading causes of electrical fires. Regular PAT testing ensures that appliances are not faulty and are unlikely to cause a fire.
Insurance Requirements
Many commercial insurance policies require businesses to carry out regular PAT testing. Failing to do so could result in a lack of coverage if an accident were to occur. Regular PAT testing helps businesses stay compliant with their insurance policy and avoids potential disputes in the event of an accident.
Maintaining Business Operations
Faulty electrical equipment can disrupt business operations. For example, an appliance failure could lead to downtime, reducing productivity. Regular PAT testing ensures that equipment is working correctly and helps prevent unplanned downtime.
3. Legal Requirements for PAT Testing in the UK
In the UK, PAT testing is not a legal requirement in and of itself. However, businesses are required to ensure that their electrical appliances and equipment are safe under the Health and Safety at Work Act 1974, the Electricity at Work Regulations 1989, and other relevant regulations.
Health and Safety at Work Act 1974
This act outlines the employer’s responsibility to ensure the health and safety of employees while they are at work. Part of this responsibility includes ensuring that all electrical equipment is safe to use.
Electricity at Work Regulations 1989
These regulations specify that employers must take steps to prevent the risk of electrical accidents by maintaining safe electrical systems and equipment. While these regulations don’t specifically mandate PAT testing, they do require businesses to ensure that electrical equipment is safe.
Management of Health and Safety at Work Regulations 1999
This regulation requires employers to assess and manage risks, including those associated with electrical appliances. A PAT test provides documentation of electrical safety, helping employers meet their obligations to assess and manage electrical risks.
4. How Often Should Commercial Properties Have PAT Testing?
The frequency of PAT testing depends on several factors, including the type of equipment, its usage, and the environment in which it’s used. While the UK does not prescribe specific timelines for PAT testing, businesses should follow a risk-based approach to determine how often they conduct tests.
General Guidelines
Low-Risk Environments: In offices and other low-risk environments where electrical appliances are used infrequently, PAT testing is typically required every 2 to 4 years.
Medium-Risk Environments: In environments such as schools or shops, where electrical appliances are in regular use, PAT testing should typically be done every 1 to 2 years.
High-Risk Environments: In high-risk environments, such as construction sites, kitchens, or factories, where electrical appliances are in constant use or subjected to wear and tear, annual PAT testing may be necessary.
It is essential to review your workplace’s electrical usage, risk profile, and safety procedures to determine how often your appliances should be tested.
5. Factors Affecting the Frequency of PAT Testing
Several factors influence how often you need to carry out PAT testing on electrical appliances in your commercial property:
Type of Equipment
Fixed Equipment: Equipment that is permanently installed (e.g., built-in ovens, air conditioning units) generally requires less frequent testing than portable appliances.
Portable Appliances: Items such as computers, toasters, or power tools often need testing more regularly due to their mobility and frequent use.
Environment
Wet Environments: In areas where electrical appliances are exposed to water, such as kitchens or outdoor work areas, the risk of electrical faults increases. These environments require more frequent PAT testing.
Harsh Conditions: Workplaces with harsh conditions, such as construction sites or factories, increase the risk of wear and tear on electrical equipment, requiring more frequent checks.
Age of Equipment
Older electrical appliances are more prone to faults. As equipment ages, it may need to be tested more often, especially if it has been subject to wear and tear.
Frequency of Use
The more often an appliance is used, the higher the risk of it becoming faulty. Therefore, commercial properties with high usage should conduct PAT tests more frequently.
6. What Does a PAT Test Involve?
A typical PAT test involves both visual inspections and electrical testing. The process includes:
Visual Inspection: Checking for obvious signs of damage, such as frayed wires, cracks, exposed metal parts, or scorch marks.
Earth Continuity Test: This checks whether the appliance is properly earthed to prevent electrical shocks.
Insulation Resistance Test: Ensures that the appliance is insulated properly and prevents the risk of electric shock.
Polarity Test: Ensures that the live and neutral wires are connected correctly.
Functional Check: Verifies that the appliance works as intended.
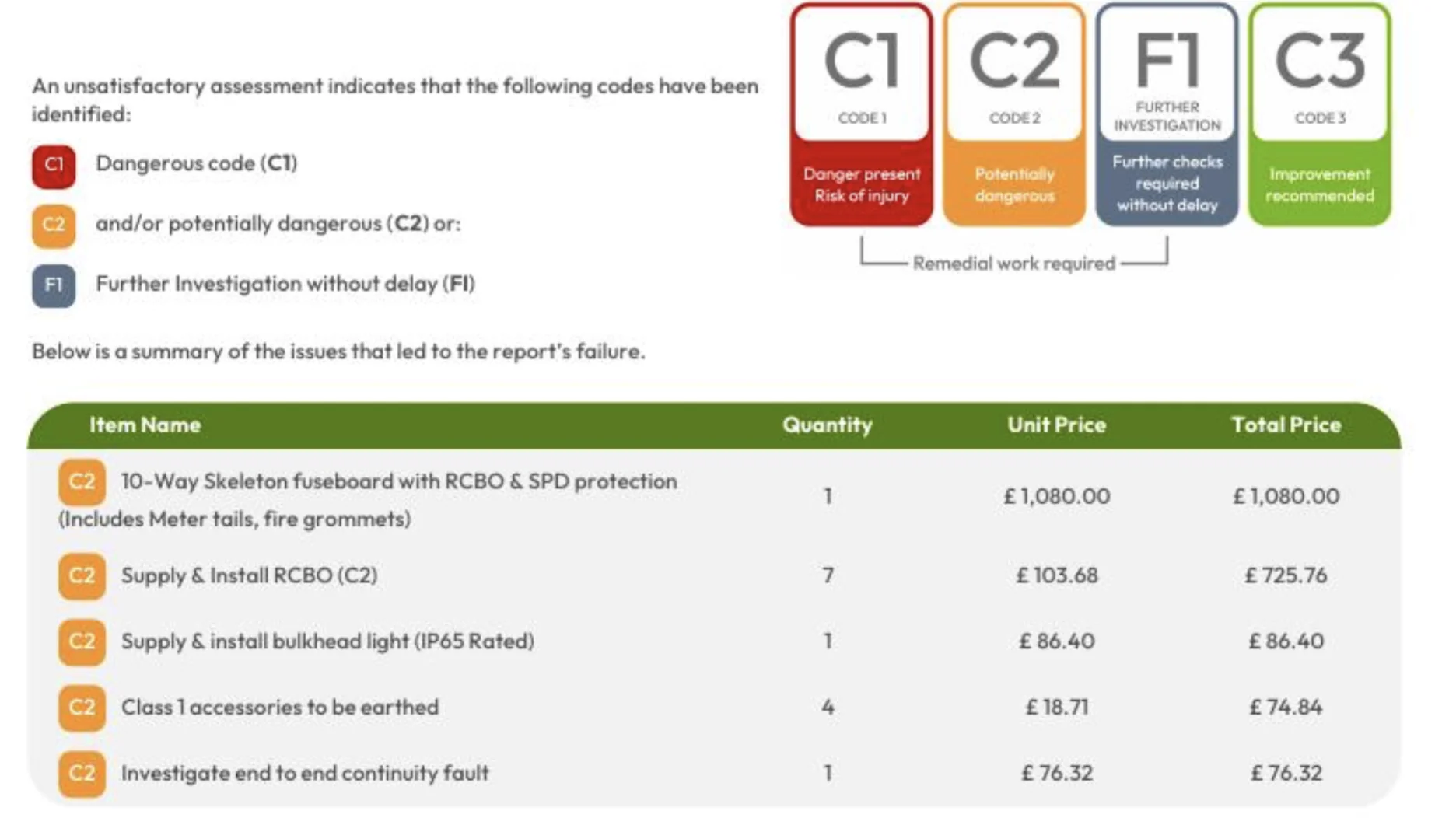
At the end of the testing process, the appliance will either pass or fail the test. A label or sticker will be placed on the appliance, indicating the date of the test and whether it passed or failed.
7. The Consequences of Failing to Carry Out PAT Testing
Failure to conduct PAT testing can result in significant consequences:
Legal Penalties
Failure to comply with Health and Safety regulations can result in legal action, including fines or penalties. In the worst-case scenario, failure to ensure electrical safety could lead to prosecutions if an accident occurs.
Increased Risk of Accidents
Without regular PAT testing, faulty electrical equipment poses a significant risk of electric shock, fires, and injuries. This could not only harm employees but also customers and visitors.
Insurance Issues
Most commercial insurance policies require businesses to maintain electrical safety. If an accident occurs and you haven’t conducted regular PAT testing, you may find yourself ineligible for insurance claims or face increased premiums.
Business Disruption
Electrical accidents caused by faulty equipment can lead to business interruptions, downtime, and lost revenue.
8. Choosing a Qualified PAT Testing Service
It is essential to hire a qualified and competent professional to perform your PAT testing. Ensure the electrician or testing service is registered with a regulatory body such as:
NICEIC (National Inspection Council for Electrical Installation Contracting)
NAPIT (National Association of Professional Inspectors and Testers)
These organizations ensure that technicians follow the correct procedures and adhere to the relevant regulations.
9. Costs Associated with PAT Testing
The cost of PAT testing depends on the number of appliances and the complexity of the testing. On average, businesses in London can expect to pay:
£50 – £150 for small offices or shops with fewer appliances
£200 – £500+ for larger commercial properties, factories, or schools
Many PAT testing companies charge a fixed price per appliance or provide a discounted rate for bulk testing.
10. Best Practices for Maintaining Electrical Safety Between PAT Tests
While regular PAT testing is essential, it’s also important to maintain electrical safety between inspections. Here are some best practices:
Inspect Appliances Regularly: Look for signs of damage such as frayed cables, scorch marks, or faulty plugs.
Encourage Proper Use: Make sure employees are trained to use electrical appliances correctly and safely.
Keep Appliances Clean and Dry: Regularly clean appliances and ensure they’re not exposed to water, moisture, or extreme temperatures.
Replace Worn-Out Equipment: Remove damaged or outdated appliances that could pose safety risks.
11. Conclusion
Ensuring the safety of electrical appliances in commercial properties is not only a legal requirement but also a critical measure to protect your employees, customers, and business assets. Regular PAT testing is essential to maintain electrical safety standards and to comply with UK regulations.
If you’re unsure of when your commercial property needs PAT testing or require professional testing services in London, Norm Electrical Engineering offers expert PAT testing solutions. Call us today at 020 8245 8400 or 0772 430 8998 to schedule a test and ensure your property remains compliant and safe.
For more information about PAT testing and legal requirements, visit the official UK government website on Electrical Safety.